Introduction:
Virtualization and containerization are two different approaches to managing IT infrastructure. While both have similar goals of improving efficiency and reducing costs, they have significant differences. This blog will provide an overview of virtualization and containerization, highlighting their differences and use cases.
Understanding Virtualization:

Virtualization creates a virtual version of a physical resource such as a server, storage device, or network. This virtual version can then be used by multiple applications or operating systems. It is achieved by installing a hypervisor on the physical machine, which creates the virtual environment. The hypervisor allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server.
Understanding Containerization:

Containerization is a lightweight alternative to virtualization. Containers are isolated from each other and share the same kernel, which makes them more efficient than virtual machines. Containers are portable, meaning they can be moved from one environment to another, making them useful for deployment in different environments.
Differences between Virtualization and Containerization:
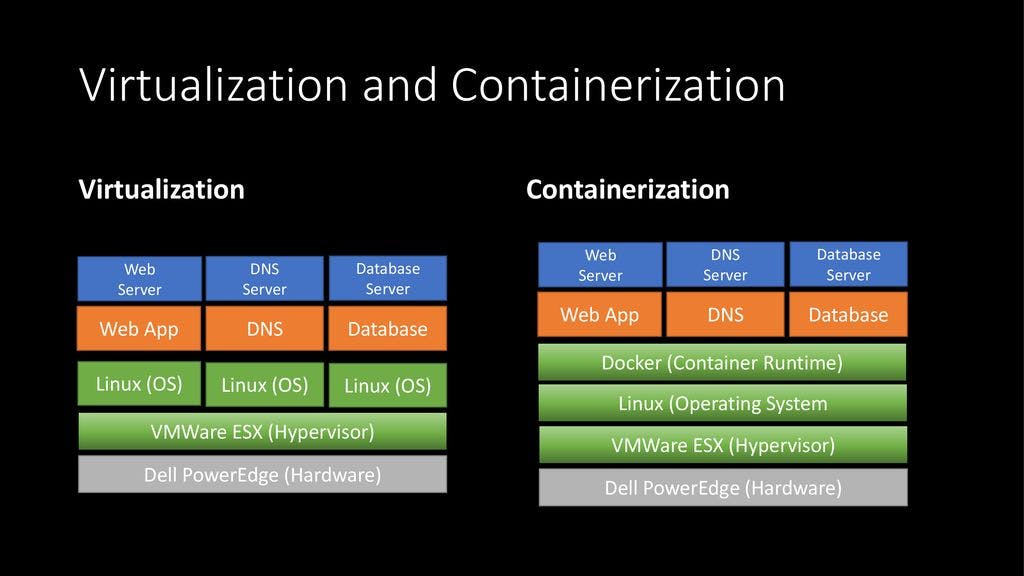
Resource Allocation: In virtualization, the hypervisor allocates resources to each VM, creating a separate environment for each VM. In contrast, containerization shares the host OS's kernel, which reduces the overhead associated with running multiple VMs.
Performance:

Containerization is more efficient than virtualization, as it eliminates the need for a hypervisor, which consumes system resources. Containers also start up and shut down faster than VMs.
Security:

Virtualization provides more security than containerization because VMs are isolated from each other. In contrast, containers share the same kernel, making it easier for attackers to move laterally within a compromised system.
Use Cases of Virtualization and Containerization:
Data Centers:

Virtualization is commonly used in data centers to consolidate resources and improve efficiency. Containerization is also useful in data centers, as it provides a more efficient way to run microservices and other lightweight applications.
Cloud Computing:

Virtualization is widely used in cloud computing, as it enables companies to run multiple VMs on a single physical server, reducing costs and improving efficiency. Containerization is also used in cloud computing, as it provides a more efficient way to run microservices and other lightweight applications.
DevOps:
Containerization is popular in DevOps because it enables developers to package their applications and dependencies into a single container. This makes it easier to deploy applications across different environments, improving the efficiency of the development process.
Conclusion:

In conclusion, virtualization and containerization are two different approaches to managing IT infrastructure. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, and their use cases depend on the specific needs of the organization. Virtualization is more secure, while containerization is more efficient. Both approaches are useful in data centers and cloud computing, while containerization is popular in DevOps.
